Arizona’s Monsoon

Arizona resides within the North American Monsoon geographical arena. The monsoon season typically begins in early June when active thunderstorms build in central and southern Mexico. In mid- to late June, the thunderstorms move toward the International Border and into Arizona. The monsoon is a season where the dry, westerly winds (winds coming from the west) that typically persist through fall, winter and spring shift to moist, southerly winds (winds coming from the south). The incoming moisture helps build thunderstorm activity across the state.
Terminology: The term “monsoon” refers to a seasonal time of year where thunderstorms are more likely to occur. A monsoon is NOT a thunderstorm, but the monsoon season can help build thunderstorms.
Monsoon thunderstorm activity accounts for roughly half of the annual precipitation in central and northern Arizona, and two-thirds to three-fourths of the annual precipitation in southern Arizona. The short-lived, intense monsoon thunderstorms can often cause flash flooding in areas with steep terrain, low-lying roads, or normally dry washes. Lightning, hail, dust storms, and strong winds are common during the monsoon season.
Basics of the Arizona Monsoon
Click on this link to access the article
Outlook Day 1 (today) |
Outlook Day 2 (tomorrow) |
Outlook Day 3 (next day) |
 |
 |
 |
Total Monsoon Precipitation (to date)
Average Daily Dewpoint
Arizona Regional WRF Model Forecasts
Click on the image to access the Arizona WRF models
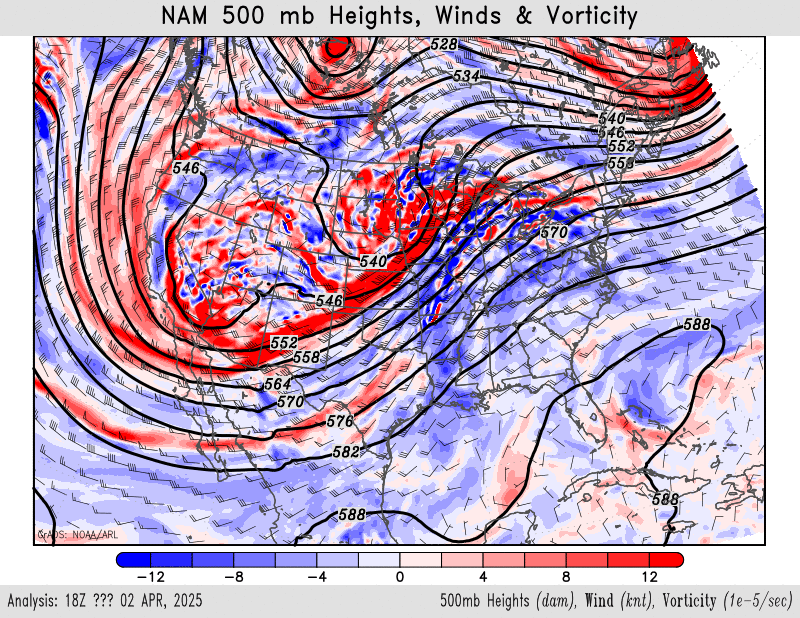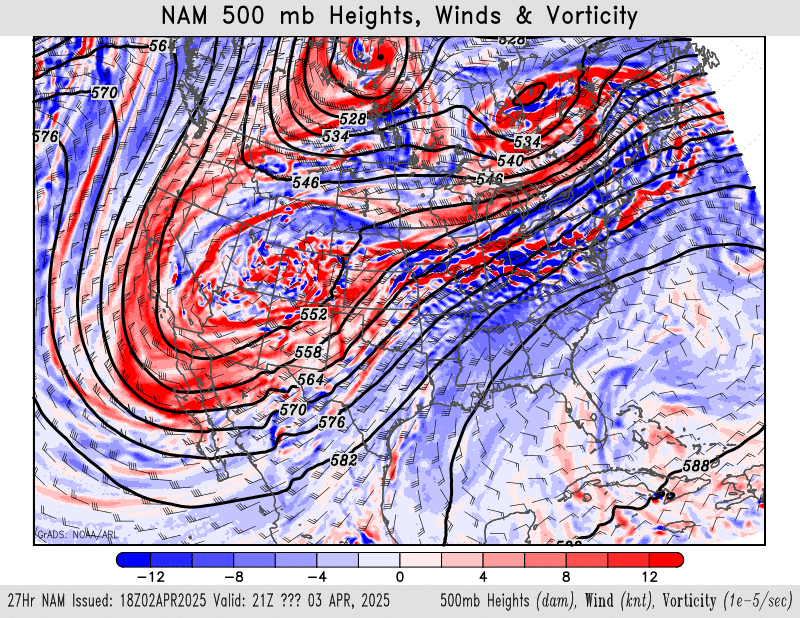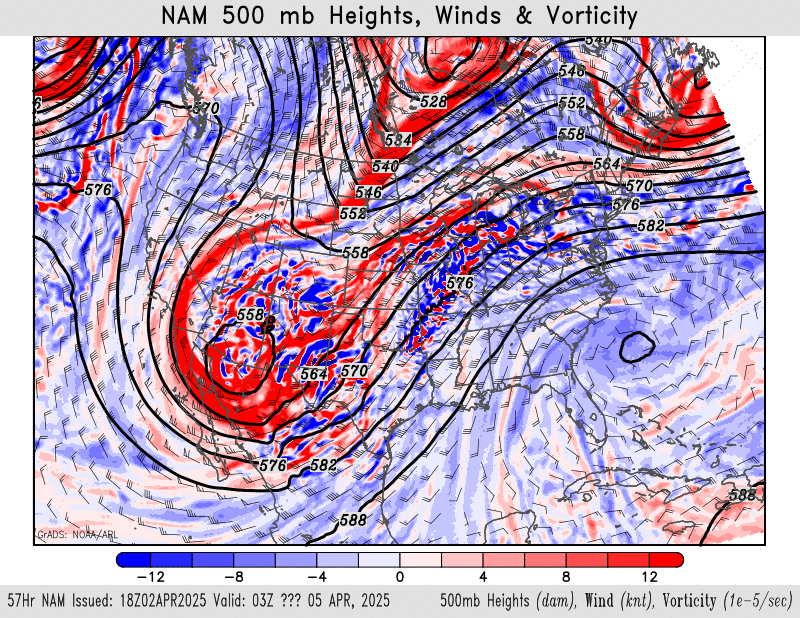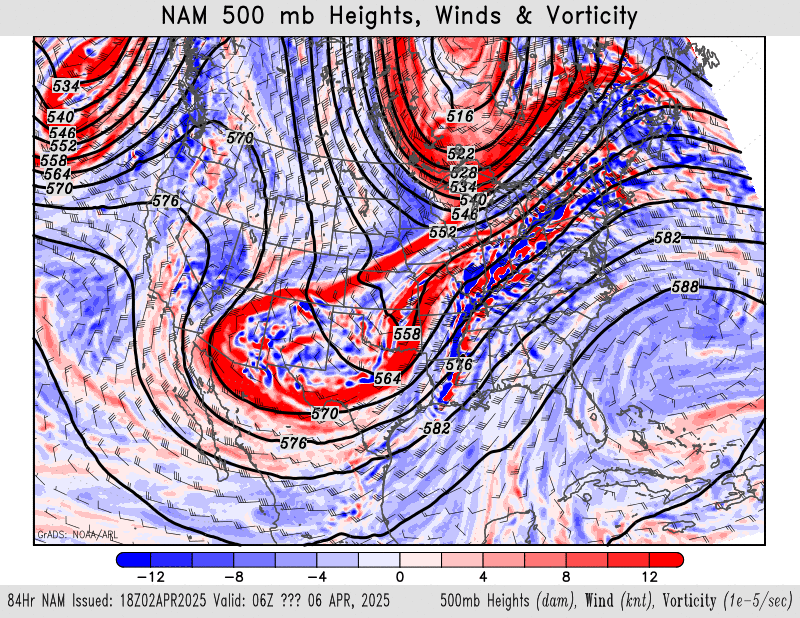
500mb height, wind, vorticity
NAM – HRRR – GFS
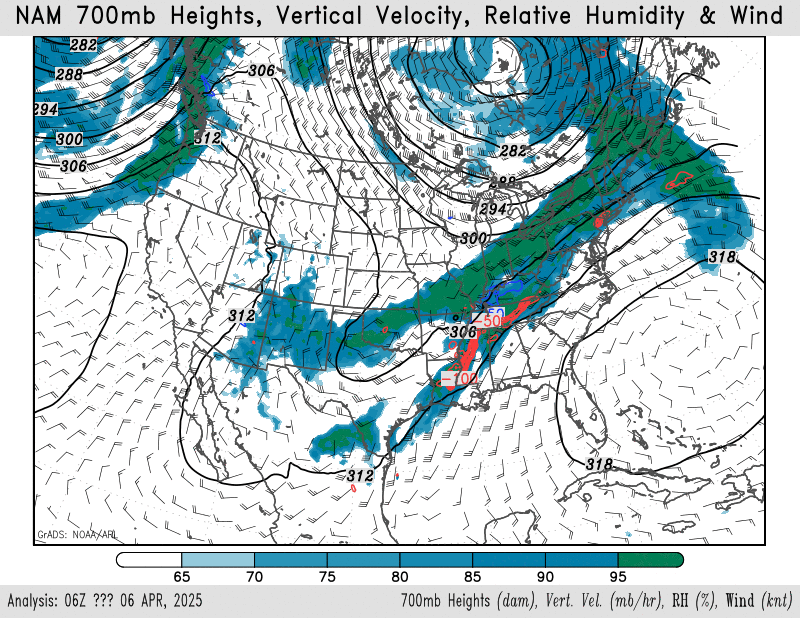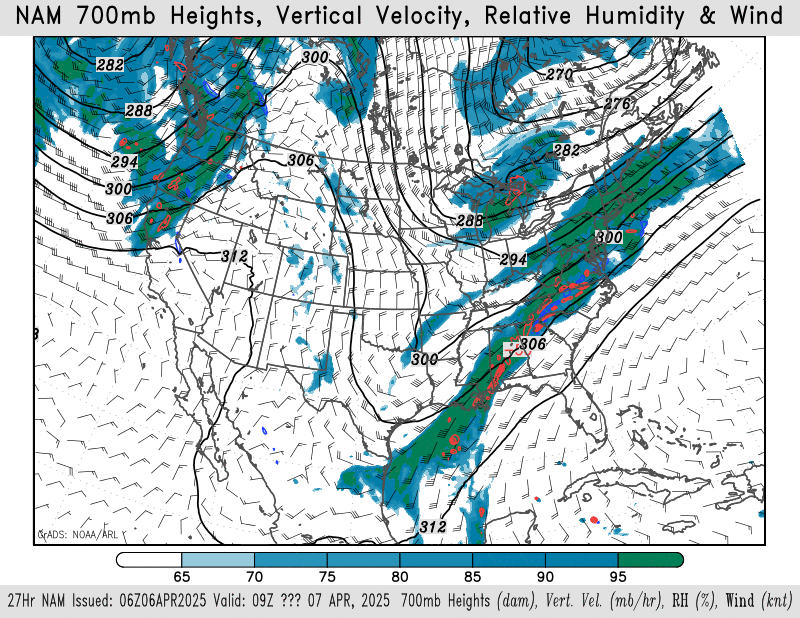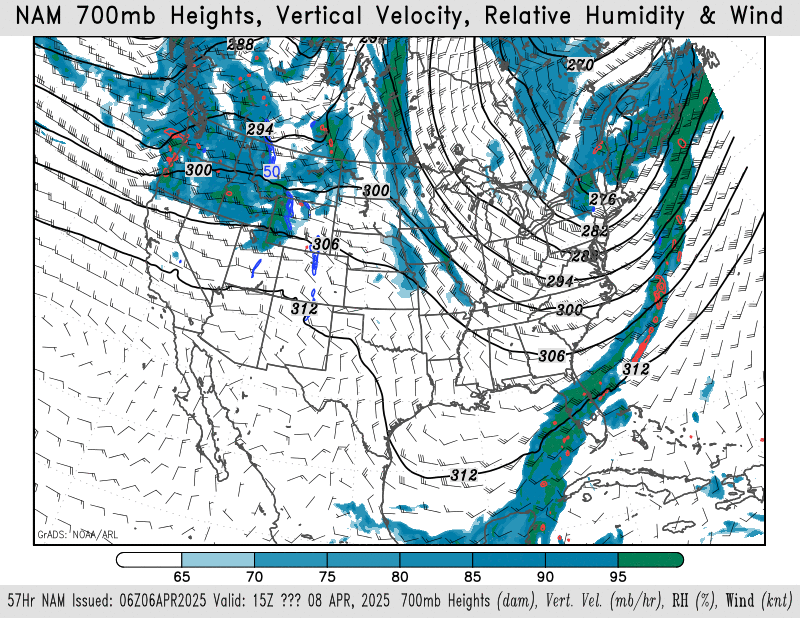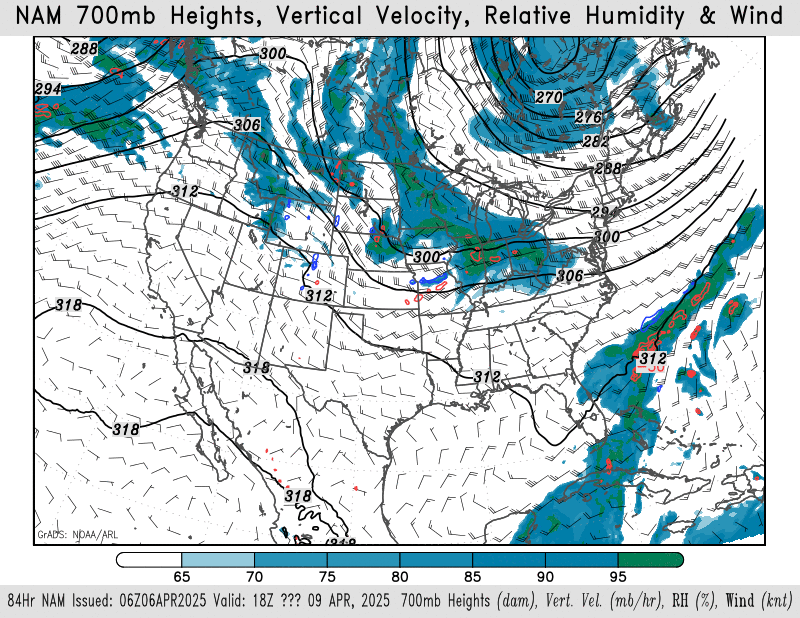
700mb height, wind, relative humidity
NAM – HRRR – GFS
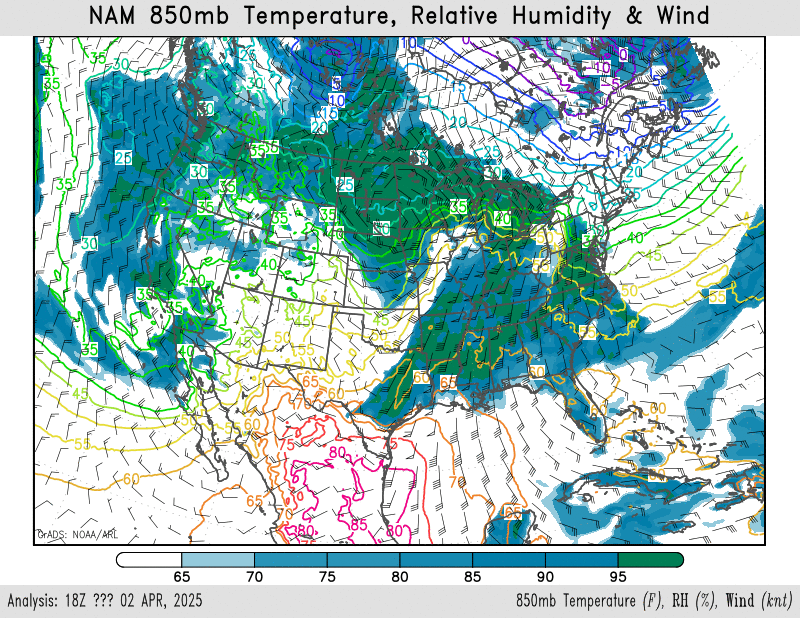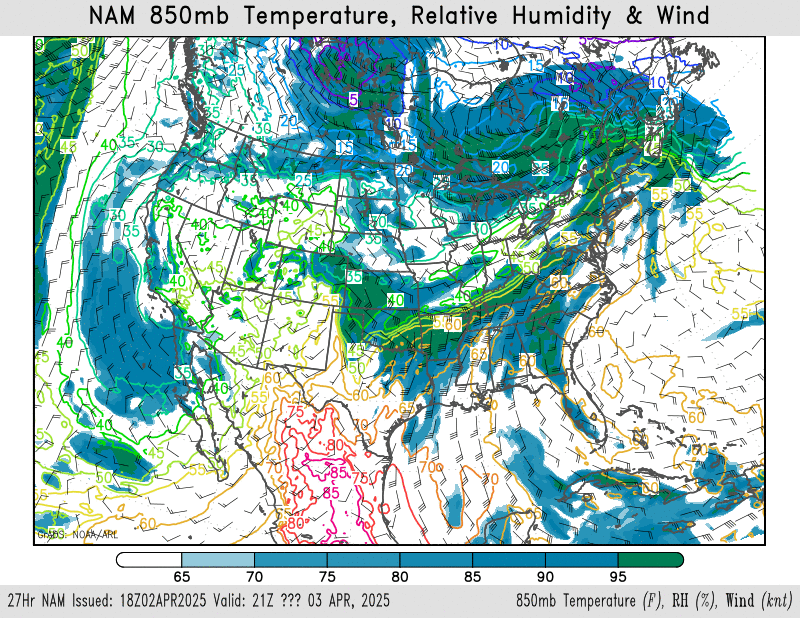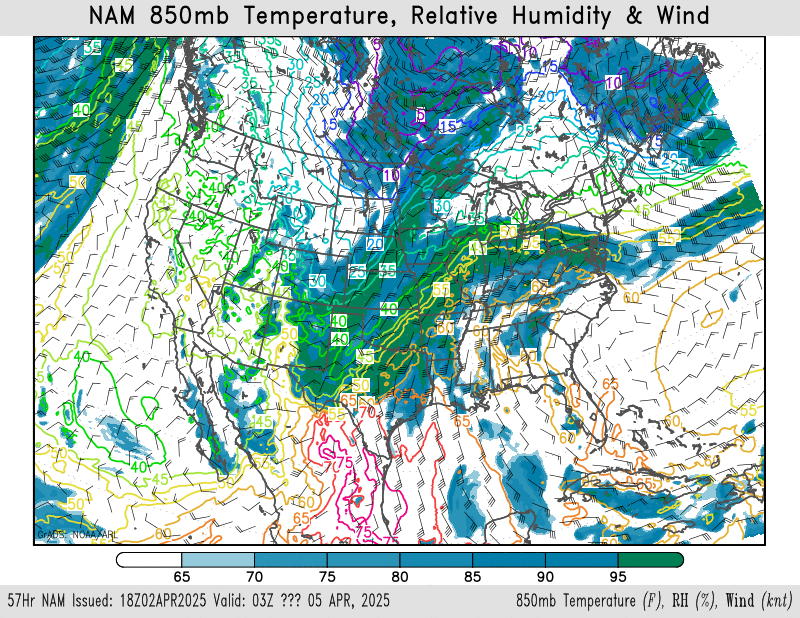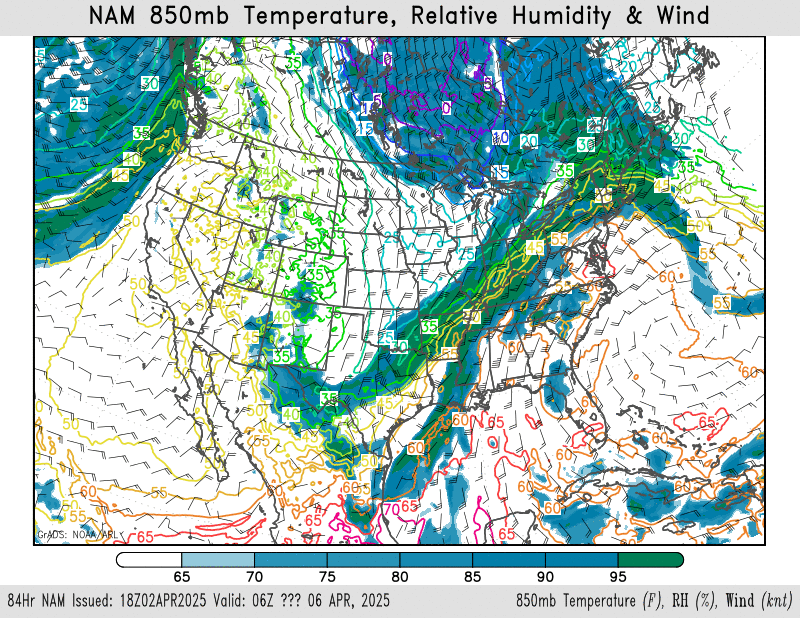
850mb temperature, relative humidity, wind
NAM – HRRR – GFS
2021 Monsoon Review
Click on this link to access the report
Monsoon Literature
Arizona and the North American Monsoon System Crimmons
Long Term Changes of Transient Inverted Troughs Lahmers, et al