Climate of Arizona
Arizona’s climate is arid and semi-arid, with average annual precipitation ranging from 3 inches in the southwest at Yuma to around 40 inches in the White Mountains in east-central Arizona. The state’s topography plays a significant role in its climate. (Arizona’s physiographic regions)
The southwestern desert is hot, with winter daytime temperatures in the lower 60s and average summer daytime temperatures between 105° and 115°F. Nighttime winter temperatures in the desert can drop slightly below freezing. Higher elevations like Alpine, AZ and Greer, AZ can reach 80°F in the summer, while winter nights in these locations frequently drop into the 20s. (Arizona’s elevations)
During June, which is the climatologically driest month (average statewide precipitation approximately 0.30 inches), the daily temperature range (maximum – minimum) frequently exceeds 40°F for much of the state.
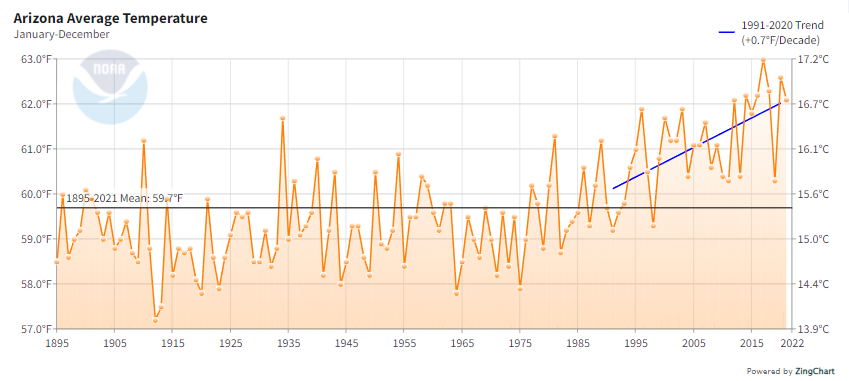
Statewide Annual Temperature
The average long-term statewide annual temperature is 59.7°F. Within the 1991-2020 climate normals, the temperature has increased by 0.7°F per decade, with the urban heat island as a large contributor.
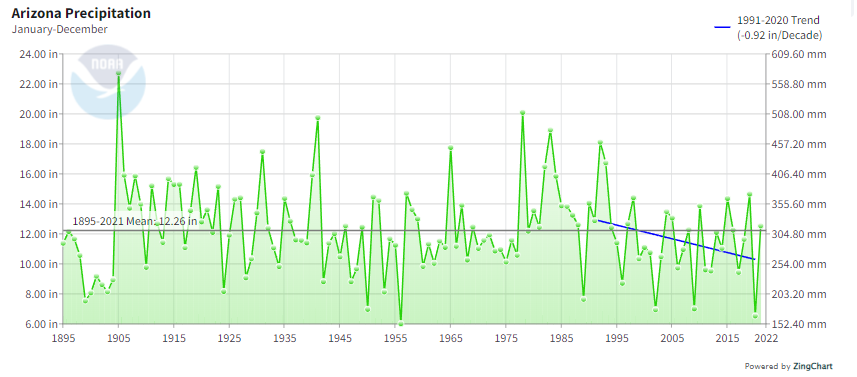
Statewide Annual Precipitation
The average long-term statewide annual precipitation is 12.26 inches. Within the 1991-2020 climate normals, the precipitation has decreased by 0.92 inches per decade. Arizona has been in a long-term drought since 1994.
Arizona State Climate Summary
Click on this image to see the latest state climate summary
Today in Arizona’s Weather History
Click on this link to see today’s weather history for Arizona
Historic Events
Click on these links for:
- Arizona Facts
- Notable Storms in the 20th Century
- Tropical Cyclones in Arizona
- Historic Extreme Temperatures in Phoenix and Yuma
- Historic First/Last Days Temperature Thresholds in Phoenix and Yuma
- Annual and Monthly Records Phoenix
- Annual and Monthly Records Yuma
- Phoenix Snowfall History
- Phoenix NWS Watch/Warning Criteria
- Phoenix NWS Storm Summaries